Nodes
Nodes are the building blocks of a workflow (a.k.a cells).
Start
Technical name: start
Every workflow must have one and only one start node.
This is a technical node which has no attributes.
End
Technical name: end
Mark the end of a workflow.
A workflow has to contain at least one end node. But it can have more than one end node. Especially in macro workflows, it is common to have multiple end nodes with names named after possible outputs.
Generic node
Except a very few of them, nodes have a generic representation.
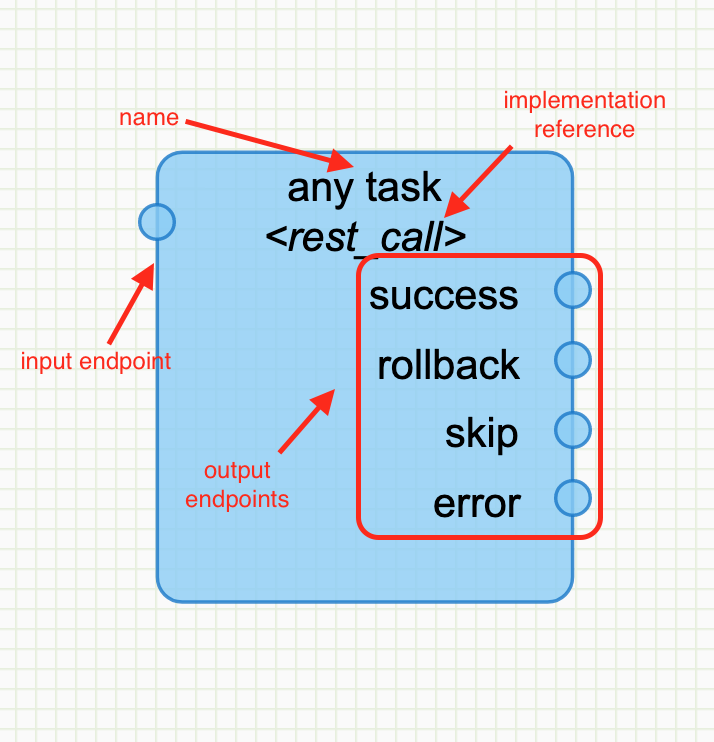
Two outputs have a special role here. When the task ends in error and skip or rollback are visible and connected, then the task details (in the instance details page) will show a button to skip and/or rollback the task alongside the Replay button.
In their details page, nodes support custom colors which allow to visually identify and group them in the workflow editor.
HTTP call
Technical name: http_call
Execute an HTTP call and assign the result to a context variable.
The call can be executed on a session holder (defined in the configuration and using a relative url) or on a new session (using a full URL, e.g http://example.com/api/users).
The result of the call is a dictionary with the following keys:
status: The HTTP status code of the response.body: The body of the response.
The result of the call is assigned to the context variable defined in the output_context_key attribute.
It can also be assigned to a cache key if the cache_key attribute is defined. If the HTTP method is GET, the result will be cached and the cache will be used for subsequent calls. If the HTTP method is not GET, the cache will be invalidated.
WARNING
If the returned status code is not in the http_codes attribute, and the error output is not linked to another node, the node will fail.
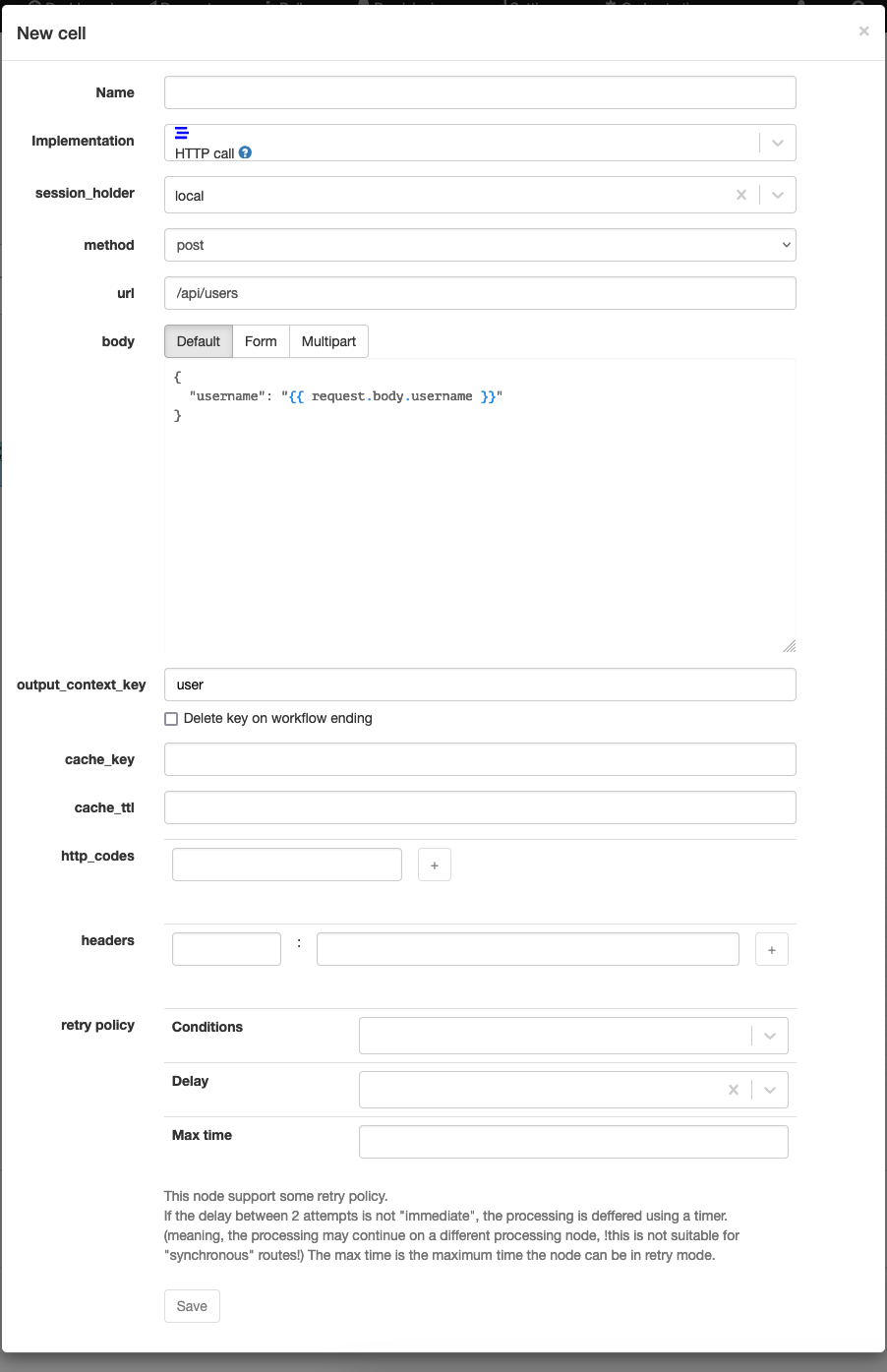
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| session_holder | The session holder to use. |
| method | The HTTP method to use. |
| url | The URL to call. |
| body | [optional] The body of the request. Default: The body is evaluated as a template and sent as such. Form: The body is sent as a HTML form data (Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded). Multipart: The body is sent as a multipart form data. Each field will be turned into a different part in the body.A file can be sent using a reference to a document attached to the instance using a reference as # documents.\<name\> |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
| cache_key | [optional] The cache key to use. |
| cache_ttl | [optional] The cache timeout to use. |
| http_codes | [optional] The HTTP codes to consider as outputs of the nodes. The * can be used to include multiple codes. |
| headers | [optional] Extra headers of the request. |
| retry policy | [optional] The retry policy to use. - Conditions: the set of criteria which will trigger a retry. - Delay: The delay to be introduced between 2 attempts. - Max time: The maximum number of attempts. |
Retry policy
If the delay is not immediate, the retry will be executed asynchronously using a timer. So the process may continue to another node. This is not suitable for synchronous calls.
REST call
Technical name: rest_call
Legacy node. It behave exactly like http_call but it extracts a special attribute _record_internal_id from the response body (this is a special case for Broadsoft gateway to link with its internal audit record for debugging).
Prefer http_call when possible.
JSON call (deprecated)
Technical name: json_call
use http_call instead.
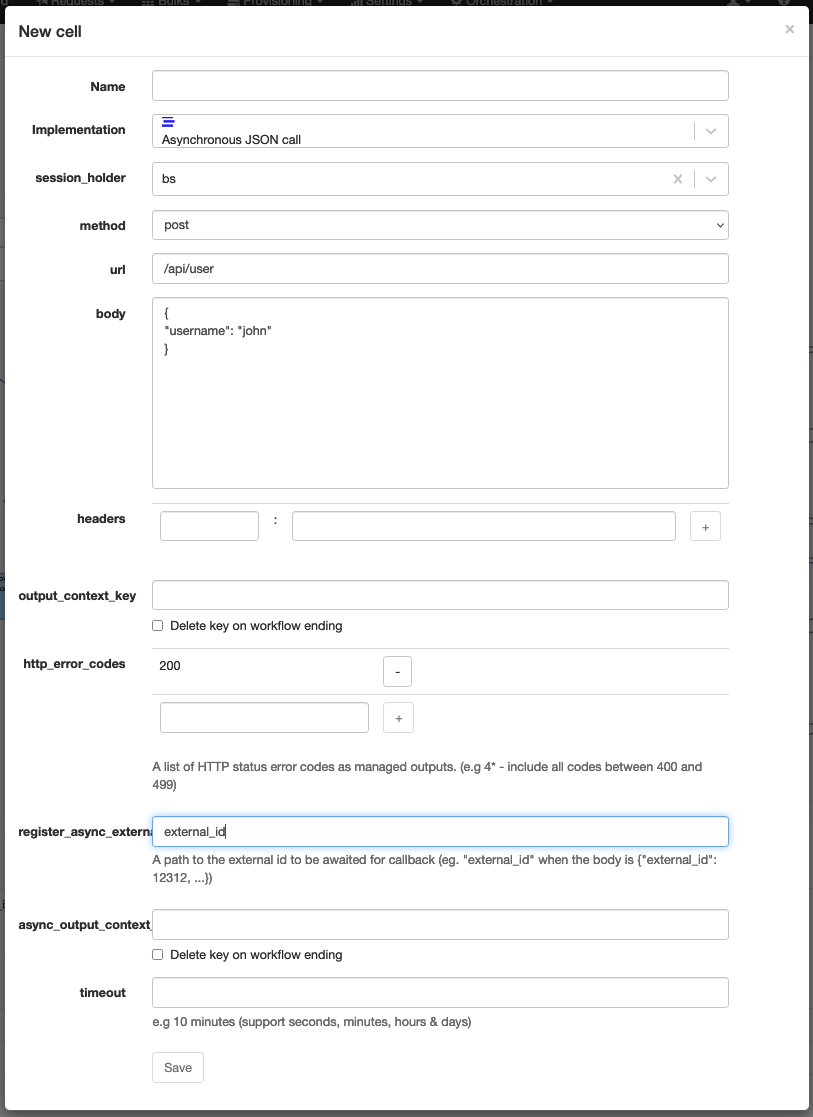
Asynchronous JSON call
Technical name: async_json_call
Execute an HTTP call with a JSON body, possibly parse its response into an object dictionary and waits for a callback to be sent with an ID matching a value present in the synchronous response.
The call can be executed on a session holder (defined in the configuration and using a relative url) or on a new session (using a full URL, e.g http://example.com/api/users).
The workflow is paused until the callback is received or the timeout is reached.
INFO
The callback needs to be sent as such:
POST /api/v01/transactions/callbacks/:callback_id HTTP/1.1
{
...
}
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| session_holder | The session holder to use. |
| method | The HTTP method to use. |
| url | The URL to call. |
| body | The JSON body of the request. |
| headers | [optional] Extra headers of the request. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
| http_error_codes | [optional] The HTTP codes to consider as outputs of the nodes. The * can be used to include multiple codes. |
| register_async_external_id | Path to the external id to be expected in the callback (e.g "external_id" if the body of the synchronous response call is {"external_id": "123465"}) |
| async_output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result of the callback to. |
| timeout | [optional] The timeout of the asynchronous call. |
Processing of the callback
When a callback is received,
- either the instance is already in the database then the external callback is created with the status
LOCKED(to mark that no other process can work on it) - or the instance is not yet persisted in the database and the processing should be postponed, then the external callback is created in status
READY(to mark the event is ready to be processed but miss an external dependency, here the instance context in the database.
The event will be processed automatically, as soon as the instance is persisted in the database.
When the processing of the external event is complete, the status move to CONSUMED.
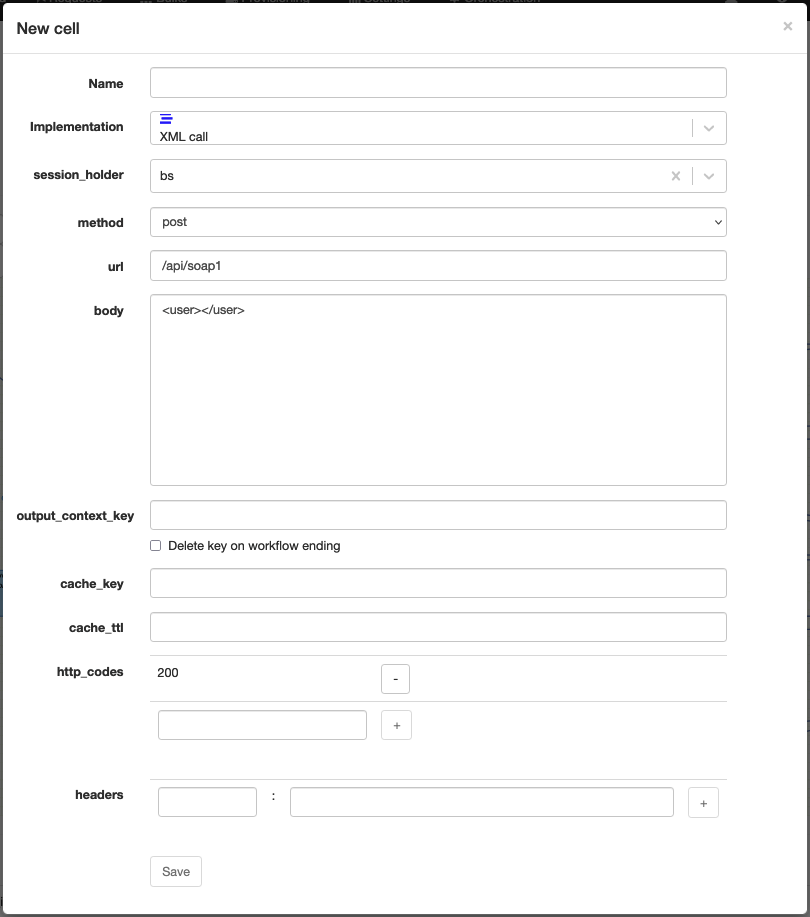
XML call
Technical name: xml_call
Execute an HTTP call with an XML body and parse its response into an object dictionary (possibly) and assign the result to a context variable.
The call can be executed on a session holder (defined in the configuration and using a relative url) or on a new session (using a full URL, e.g http://example.com/api/users).
The result of the call is a dictionary with the following keys:
status: The HTTP status code of the response.body: The body of the response.
It can also be assigned to a cache key if the cache_key attribute is defined. If the HTTP method is GET, the result will be cached and the cache will be used for subsequent calls. If the HTTP method is not GET, the cache will be invalidated.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| session_holder | The session holder to use. |
| method | The HTTP method to use. |
| url | The URL to call. |
| body | The XML body of the request. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
| cache_key | [optional] The cache key to use. |
| cache_ttl | [optional] The cache timeout to use. |
| http_codes | [optional] The HTTP codes to consider as outputs of the nodes. The * can be used to include multiple codes. |
| headers | [optional] Extra headers of the request. |
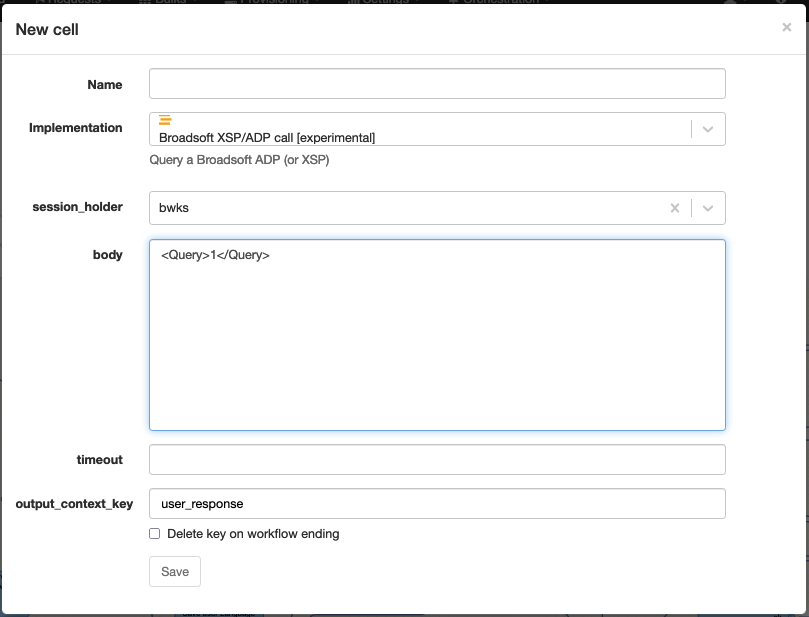
Broadsoft XSP / ADP call (experimental)
Technical name: bsft_call
Execute a Broadsoft XSP / ADP call using the OCI protocol and assign the result to a context variable.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| session_holder | One of the TCP session holders set in the configuration |
| body | The OCI body command to be sent. (do not set the "echo" attribute, it will be generated) |
| timeout | [optional] The timeout of the query. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
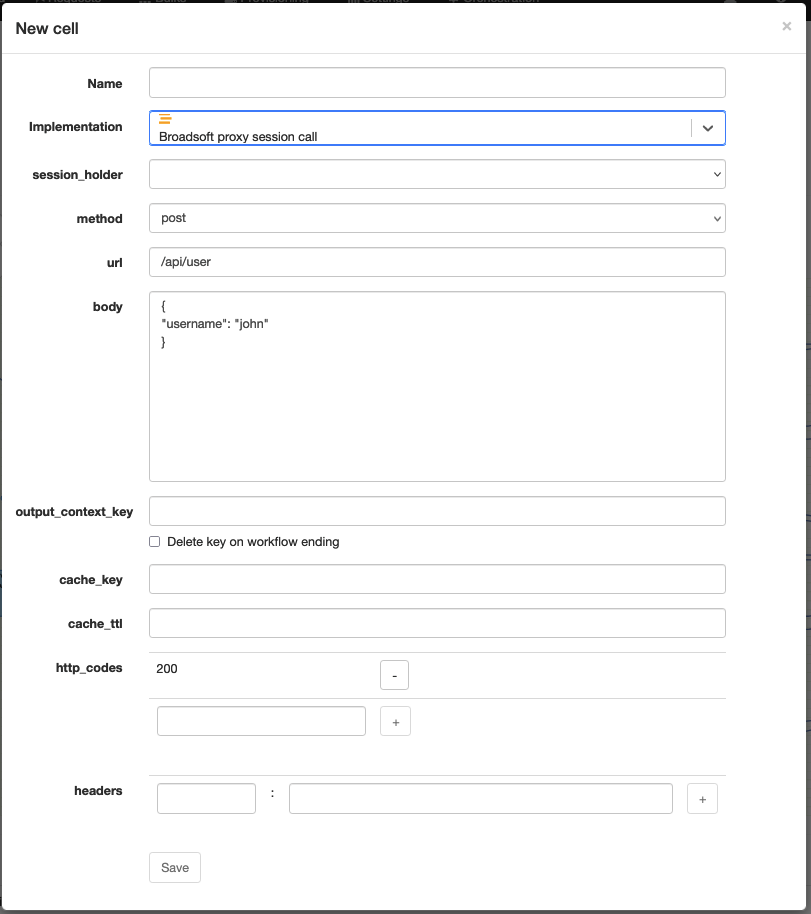
Broadsoft proxy session call
Technical name: proxy_session_call
Execute a call on a Broadsoft gateway using the instance owner session.
This node is meant to be executed on a Core instance running with a proxy mapping set. So the Broadsoft gateway will be called using this mapping.
TIP
When the session holder has the value "original user or system", the call will be executed using the original user session if it exists, otherwise it will be executed using the system session. So the call will fail if the original user session is not allowed to do the call, it will not fallback to the "system" level session.
WARNING
The node rely on the currently running session of the user. If the user is not logged in or his session is expired, the node will fail. So it's recommended to use this node in a workflow which is triggered by a synchronous call. It may also limit the possibility to replay the workflow.
WARNING
That node is affected by an old time bug which always produce a body as a string.
So interracting with the body would need to use | json to dig into it (e.g {{ (output.body | json).attribute... }}). Solving that bug would break too many existing workflows for now.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| session_holder | The directive to pick the right session: * system: use the system level session * original user or system: use the user session if it exists or the system level session * original user or fail: use the user session if it exists or the node fails |
| method | The HTTP method to use. |
| url | The URL to call. |
| body | The body of the request. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
| cache_key | [optional] The cache key to use. |
| cache_ttl | [optional] The cache timeout to use. |
| http_codes | [optional] The HTTP codes to consider as outputs of the nodes. The * can be used to include multiple codes. |
| headers | [optional] Extra headers of the request. |
Proxy HTTP call
Technical name: proxy_call
Forward an HTTP call to another URL o an session holder.
The result of the call is a dictionary with the following keys:
status: The HTTP status code of the response.body: The body of the response.
It can also be assigned to a cache key if the cache_key attribute is defined. If the HTTP method is GET, the result will be cached and the cache will be used for subsequent calls. If the HTTP method is not GET, the cache will be invalidated.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| session_holder | The session holder to use. |
| url_substitution_re | A regular expression to replace the URL. |
| source | The source object of the call, usually {{ request }}. The source element needs to contain the following keys: * url * method * [optionally] content_type |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
| http_codes | [optional] The HTTP codes to consider as outputs of the nodes. The * can be used to include multiple codes. |
| cache_key | [optional] The cache key to use. |
| cache_ttl | [optional] The cache timeout to use. |
TCP call (experimental)
Technical name: tcp_call
Execute a TCP call and assign the result to a context variable.
The body is a string that will be sent to the TCP server.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| session_holder | One of the TCP session holders set in the configuration |
| body | The body to be sent. |
| timeout | [optional] The timeout of the query. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
| output_hex | Whether the output should be converted to hexadecimal in the result. |
Cleanup cache
Technical name: cleanup_cache
Invalidate a set of cache keys.
Context setter
Technical name: context_setter
Set a context variable to a value.
If the key already exists, it will be overwritten.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| key | The context variable to set. |
| value | The value to set. |
Multiple context setter
Technical name: multi_context_setter
Set multiple context variables to values at once.
If a key already exists, it will be overwritten.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| entries | A dictionary of values to set. |
Synchronous response
Technical name: sync_response
Set the response of the synchronous call.
Internally, it behaves like the Context setter, but sets the *sync_response* context variable. This variable is used by the synchronous call to set the response.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| body | The body of the response. If it starts with [ or {, the node assumes the body is a JSON string, otherwise it's a raw string. |
| status | The status code of the response. |
Callback response
Technical name: callback_response
Set the response / result of a sub-workflow as a callback to its parent workflow.
Internally, it behaves like the Context setter, but sets the *cb_response* context variable. This variable can be used in the context of the parent workflow.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| body | The body of the response. If it starts with [ or {, the node assumes the body is a JSON string, otherwise it's a raw string. |
| status | The status code of the response. |
Trigger manual action
Technical name: trigger_manual_action
Trigger a manual action.
The manual actions will pause the workflow until the user executes the action.
The request detail page will display the manual actions that are waiting for a user action. And let the user execute them.
A manual action is usually associated to a user role. So only users with the role will be able to execute the action. A mail can be sent to the users with that role when the action is triggered.
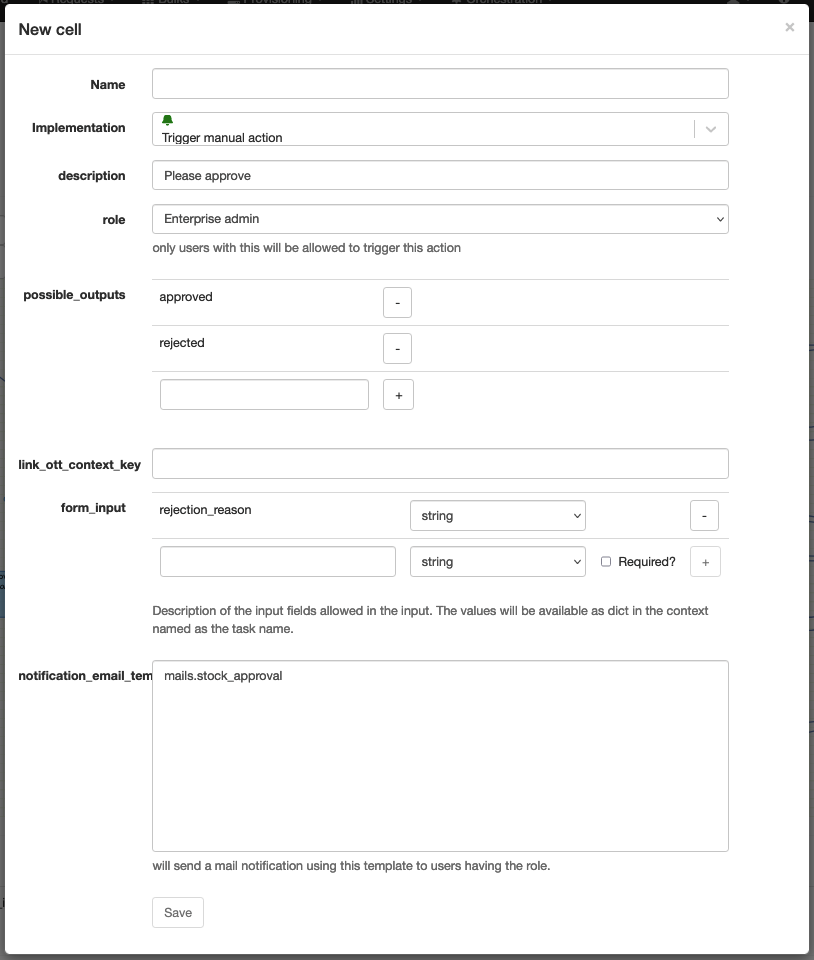
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| description | The description of the manual action. |
| role | The role of the users that can execute the action. |
| possible_outputs | The possible outputs of the action. |
| link_ott_context_key | [optional] The context variable to link one-time token to. |
| form_input | [optional] a set of fields to be filled by the user when executing the action. |
| notification_email_template | [optional] The mail template to send to the users with the role. |
See the manual actions section for more details about the setup and the usage.
Cancel manual action
Technical name: cancel_manual_action
Cancel a manual action.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| description | The description of the manual action to cancel. |
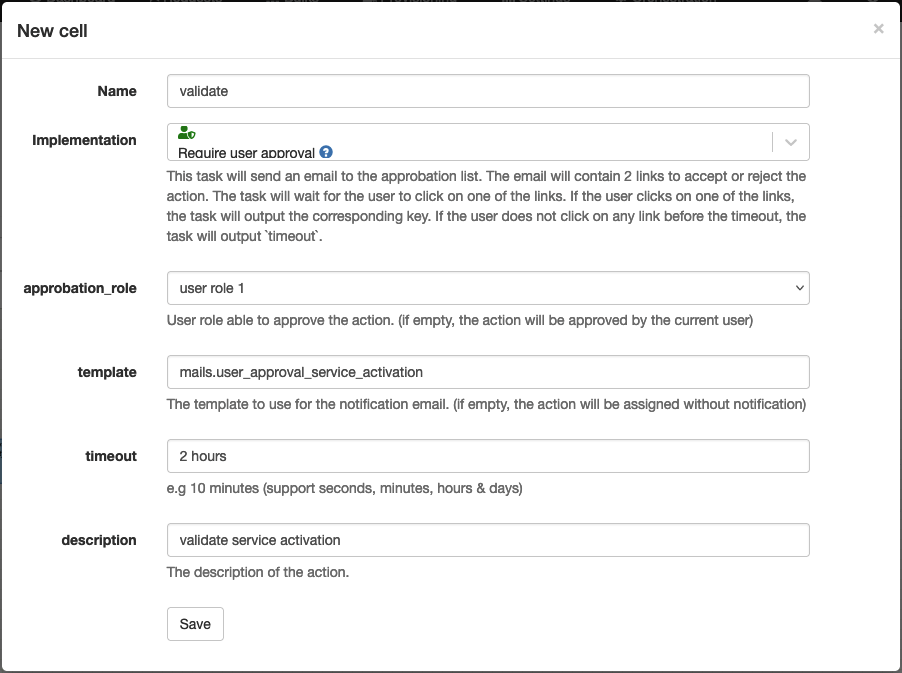
Require user approval
Technical name: user_approval
The node will pause the workflow until a user approves or declines the action.
The action is assigned to a user role or to the owner of the instance.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| approbation_role | The role of the users that can approve the action. (if empty, the action is assigned to the instance owner) |
| template | The template to use for the notification email (if empty, there is no notification sent) |
| timeout | The timeout of the approval. (instance continues with the timeout output) |
| description | The description of the approval action. |
The email template used for notification is resolved in the context of the instance, and the following variables are also available:
to: The destination of the mail.from: The sender of the mail.action_guid: The GUID of the action.instance_guid: The GUID of the instance.action_path: The API link to the action (e.g /api/v01/transactions/guid/actions/guid).outputs: The possible outputs of the action (approvedanddeclined).
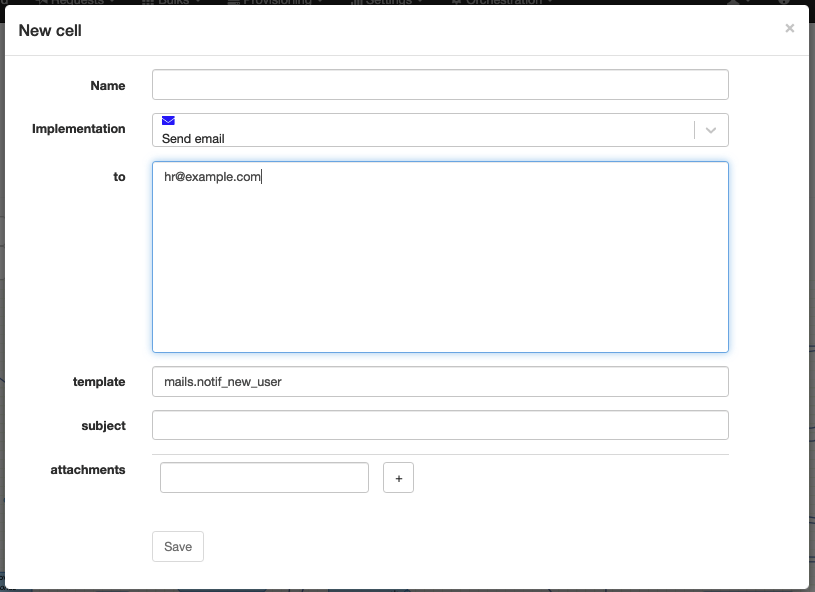
Send email
Technical name: send_email_template
Send a mail using a template. The template is resolved in the context of the instance.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| to | The destination list of the mail. |
| template | The template to use. |
| subject | [optional] The subject of the mail. |
| attachments | [optional] A list of attachments to add to the mail. These are documents created or managed in the context of the instance. |
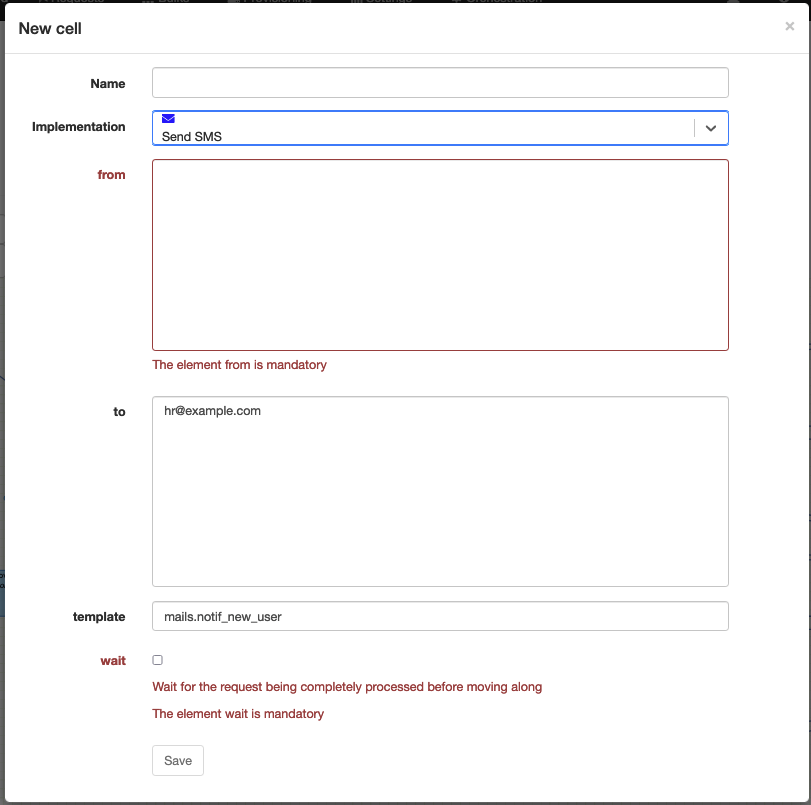
Send SMS
Technical name: send_sms
Send an SMS using the SMPP gateway configured in the configuration.
The body is a template resolved in the context of the instance.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| from | The sender of the SMS. |
| to | The destination list of the SMS. |
| template | The template body of the SMS. |
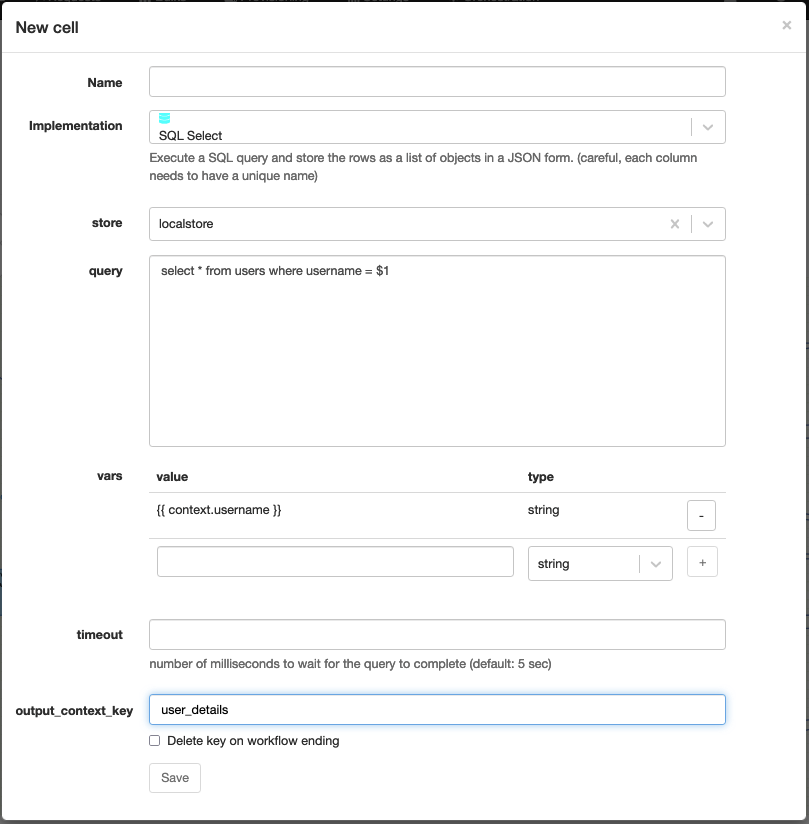
SQL Select
Technical name: sql_select
Execute a SQL query and assign the result to a context variable.
DANGER
For security reasons, it's highly recommended to use variables in the query instead of directly using the query attribute (avoid SQL injections with improper inputs).
The result of the query is a list of rows. Each row is a dictionary with the column names as keys.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| store | The datastore to use. |
| query | The SQL query to execute. |
| vars | [optional] A list of variables to use in the query. |
| timeout | [optional] The timeout of the query. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
SQL Exec
Technical name: sql_exec
Execute an SQL query which has nothing in the response.
DANGER
For security reasons, it's highly recommended to use variables in the query instead of directly using the query attribute (avoid SQL injections with improper inputs).
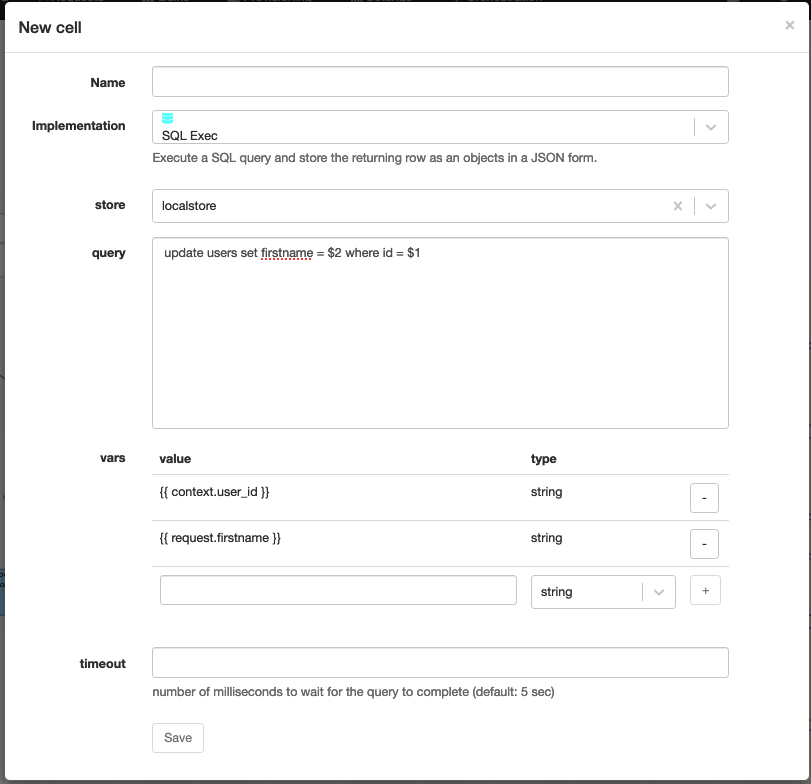
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| store | The datastore to use. |
| query | The SQL query to execute. |
| vars | [optional] A list of variables to use in the query. |
| timeout | [optional] The timeout of the query. |
SQL Exec with return
Technical name: sql_exec_with_return
Execute an SQL query and fetch its returning data.
DANGER
For security reasons, it's highly recommended to use variables in the query instead of directly using the query attribute (avoid SQL injections with improper inputs).
The result of the query is a JSON object with columns as keys.
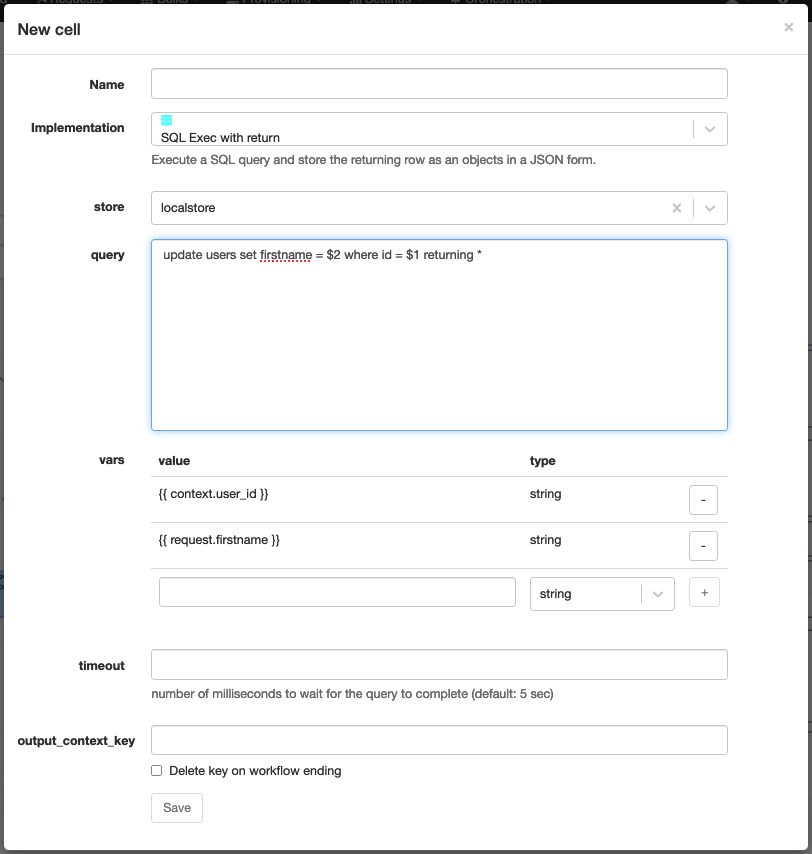
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| store | The datastore to use. |
| query | The SQL query to execute. |
| vars | [optional] A list of variables to use in the query. |
| timeout | [optional] The timeout of the query. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
Boolean expression
Technical name: boolean_expression
Evaluate a boolean expression and trigger a different path depending on the result (true or false).
INFO
Boolean expression is evaluated in the context of the current request as Jinja2 template and Python3 expression.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| expression | The boolean expression to evaluate. |
Switch
Technical name: switch
Execute a different path depending on the evaluation of a set of conditions.
Conditions are boolean expressions resolved in order. The first condition which evaluates to true will be executed. If no condition evaluates to true, the "default" path will be executed.
INFO
Boolean expressions are evaluated in the context of the current request as Jinja2 templates and Python3 expressions.
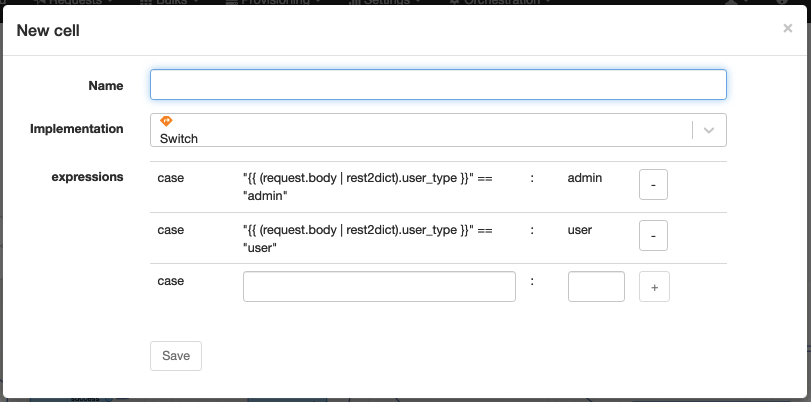
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| expressions | A list of boolean expressions to evaluate. |
Or
Technical name: or_outputs
Wait for one of the inputs to be executed before continuing the workflow. Only one input will pass through the node and continue the execution.
Join
Technical name: sync_outputs
Wait for multiple inputs to be executed before continuing the workflow. All inputs must be executed before the workflow can continue.
Timer
Technical name: timer
Wait for a certain amount of time. If the timer is shorter than 20s it will be executed synchronously. Otherwise it will be executed asynchronously. When the timer is synchronous, it can't be stopped.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| timeout | The duration of the timer. This is a string representing a duration (e.g 2 sec, 3 min). |
| discard_idle_limit | Discard the internal behaviour to keep the timer synchronous if the timeout is less than 20s. |
Context timer
Technical name: context_timer
Use a context variable to define the start and the duration of the timer.
TIP
Multiple timers can be started with the same key. If a timer is started with the same key as an active timer, the active timer can be cancelled.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| variable | The start of the timer. This is a string representing a date (e.g 2021-01-01 00:00:00). |
| timeout | The duration of the timer. This is a string representing a duration (e.g 2 sec, 3 min). |
| key | [optional] A timer key identifier |
| cancel_active_key | Whether to cancel active timers with the same key. |
Stop timer
Technical name: stop_timer
Stop a timer.
Generate OTT
Technical name: generate_ott
Generate a one-time token and assign it to a context variable. One-time token are useful to generate a link to an action which can only be used once (e.g reset a user password).
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| scope | The scope of the generated one-time token. This is a string which is used to identify the action to perform. (a manual action, a reset password etc...) |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the generated one-time token to. |
| expiry_date | [optional] The expiry date of the generated one-time token. This is a time duration. It can a be a number (interpreted as a number of seconds) or it's parsed using time.ParseDuration. |
| details | [optional] Additional details to store with the generated one-time token. This is a JSON object. |
TIP
The default expiry date for reset password one-time token is 20 minutes.
Generate random string
Technical name: generate_random_string
Generate a random string and assign it to a context variable.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| lowercase | Whether to include lowercase characters in the generated string. |
| uppercase | Whether to include uppercase characters in the generated string. |
| digits | Whether to include digits in the generated string. |
| special_chars | Whether to include special characters in the generated string. Here the special character set: !@#$%&*. |
| length | The length of the generated string. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the generated string to. |
Create QR code
Technical name: create_qr
Create a QR code image and attach it to the current context as PNG encoded in base64.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| content | The content of the QR code. It can be a text, an URL or any string content. |
| width | The width of the QR code. |
| height | The height of the QR code. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the QR code to. |
Set Request status
Technical name: set_request_status
Assign a status to the current request.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| status | The status to assign to the current request. |
Set task status
Technical name: set_task_status
Change the status of a task. This is useful to mark a task in error and allow the user to replay a certain task in the workflow.
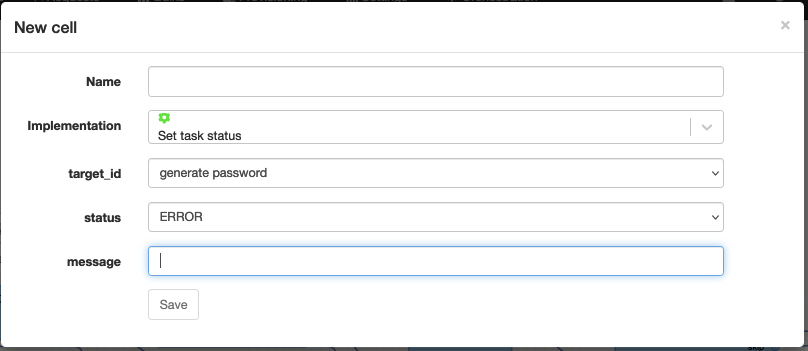
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| target_id | The name of the task to change the status of. |
| status | The status to assign to the task. (ERROR or OK) |
| message | The error description. |
Macro
Technical name: macro
Execute a subworkflow on a single input.
The name of the end node of the subworkflow will be used as the output of the macro node.
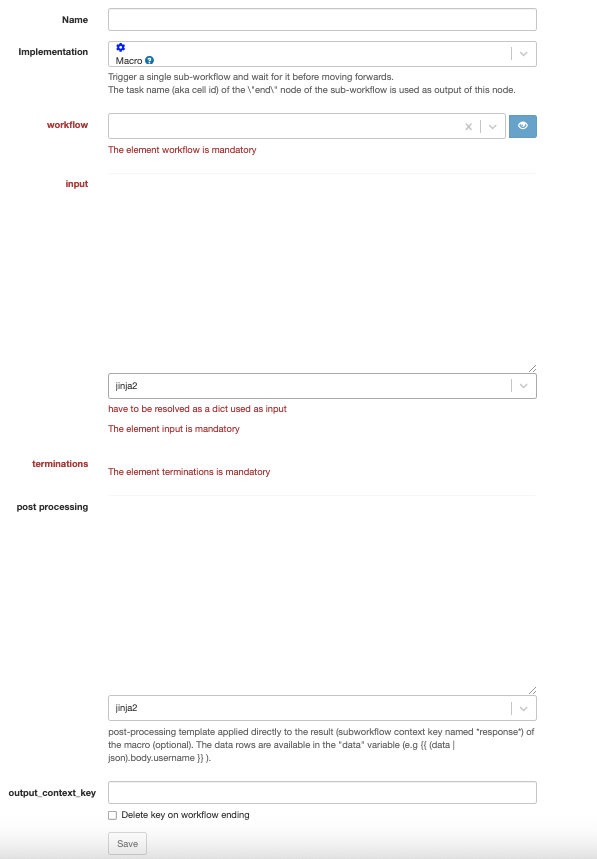
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| workflow | The subworkflow to execute. |
| input | The input to pass to the subworkflow as request. |
| terminations | The possible 'end' of the subworkflow as outputs of the macro node. |
| post processing | Optional template applied directly to the result (subworkflow context key named response) of the macro. The data rows are available in the "data" variable (e.g {{ (data | json).body.username }} ). |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the output of the subworkflow to. (read, the value of the context key *cb_response* set by the subworkflow) |
Subworkflow
Technical name: trigger_subworkflows
Execute multiple subworkflows on a list of inputs.
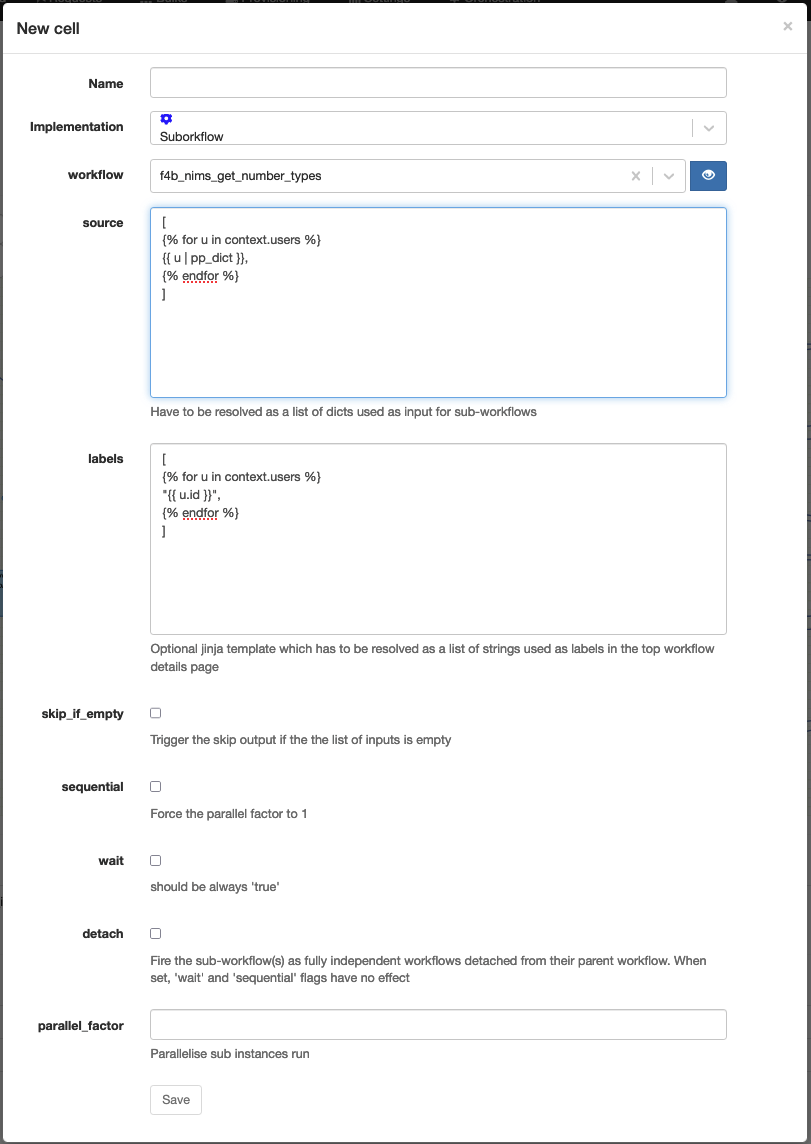
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| workflow | The subworkflow to execute. |
| source | The list of inputs to pass to the subworkflow as request. |
| labels | [optional] The labels to assign to the subworkflow. If set, the number of labels has to perfectly match the number of inputs in the source. If it isn't, a simple incremental counter is used as label |
| skip_if_empty | Whether to use the skip output if the source is empty. |
| sequential | force the parallel_factor to 1. So it executes workflow in order 1-by-1. |
| wait | [deprecated] no effect. |
| detach | [deprecated] no effect. |
| parallel_factor | The number of subworkflows to execute in parallel. |
Create user
Technical name: create_user
Create a new user locally on the system.

| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| username | The username of the new user. |
| The email address of the new user. | |
| firstname | The first name of the new user. |
| lastname | The last name of the new user. |
| mobile | The mobile number of the new user. |
| ui_profile | The UI profile of the new user. This only influence the view of the user in the APIO core UI. |
| profile_id | The profile of the new user. This is the profile of the user in the APIO core engine. |
| properties | The properties of the new user. This is a JSON object. |
| user_id_context_key | The context variable to assign the user ID to. |
| password_context_key | The context variable to assign the password to. |
| auth_backend | The authentication backend to use. This is the name of the authentication backend as defined in the APIO core configuration. |
| entity | The entity of the new user. If it's set, the user is treated as a technical user for M2M exchanges. |
| force_password_change | Whether to force the user to change his password at the next login. |
Update user
Technical name: update_user
Update a user locally on the system.
TIP
Empty fields are not updated.
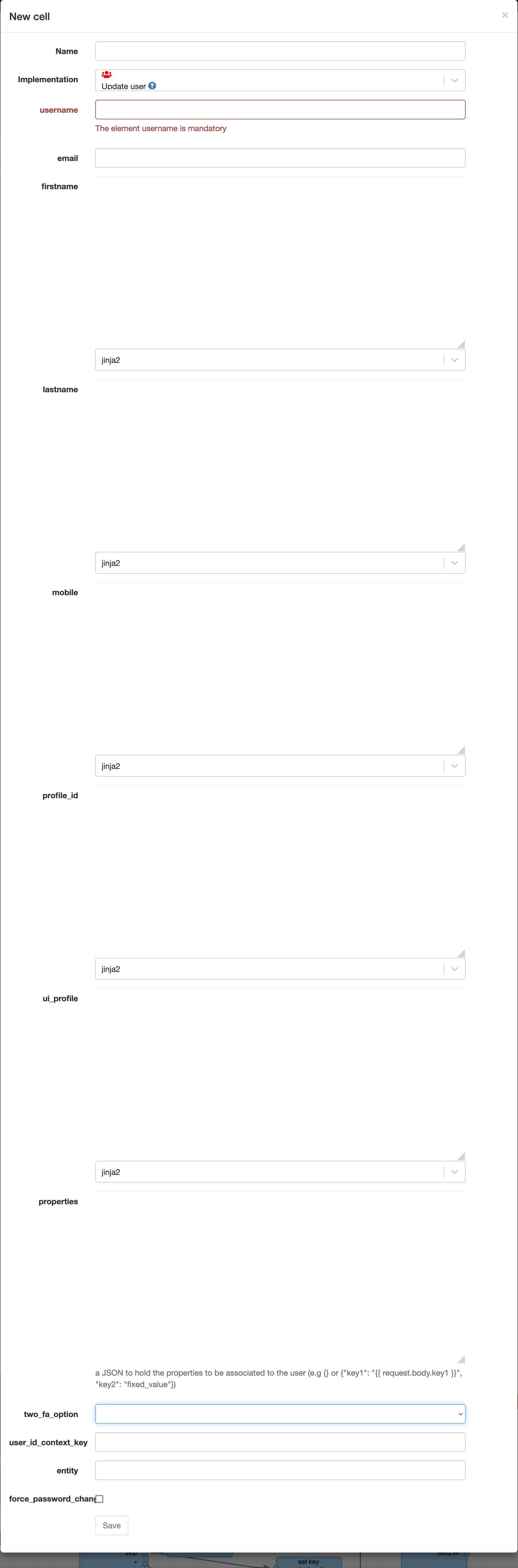
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| username | The username of the user to identify it. |
| The email address of the user. | |
| firstname | The first name of the user. |
| lastname | The last name of the user. |
| mobile | The mobile number of the user. |
| profile_id | The profile of the user. This is the profile of the user in the APIO core engine. |
| ui_profile | The UI profile of the user. This only influence the view of the user in the APIO core UI. |
| properties | The properties of the user. This is a JSON object. |
| user_id_context_key | The context variable to assign the user ID to. |
| two_fa_option | The 2FA option to assign to the user (only email is available) |
| user_id_context_key | The context variable to assign the user ID to. |
| entity | The entity of the user. If it's set, the user is treated as a technical user for M2M exchanges. |
| force_password_change | Whether to force the user to change his password at the next login. |
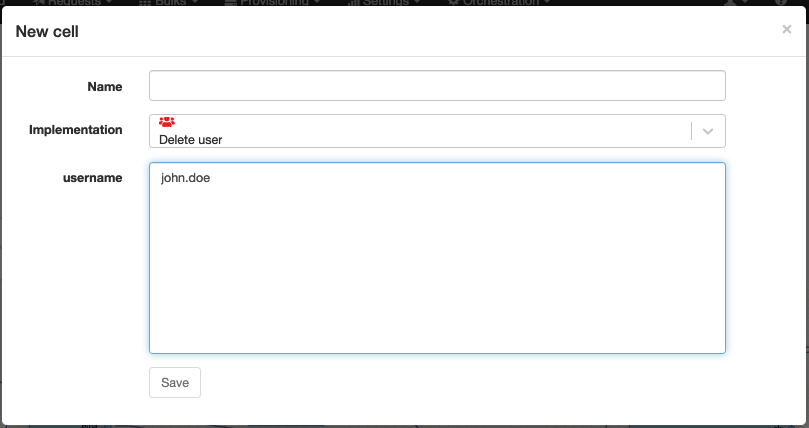
Delete user
Technical name: delete_user
Delete a user locally on the system.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| username | The username of the user to delete. |
Get owner (deprecated)
Technical name: get_owner
Get the owner of the current request. Use {{ user }} (see template variables) in your template to access the owner attributes instead.
Search transactions
Technical name: search_transactions
Search instances in the APIO core engine database.
The result is a list of instances matching the query.
The query supports the following criteria:
- instance_id: the ID of the instance
- guid: the GUID of the instance
- status: the status of the instance
- activity_id: the ID of the activity
- activity: the name of the activity
- user_id: the ID of the owner of the instance
- label: the label of the instance
- created_on: the creation date of the instance
- updated_on: the last update date of the instance
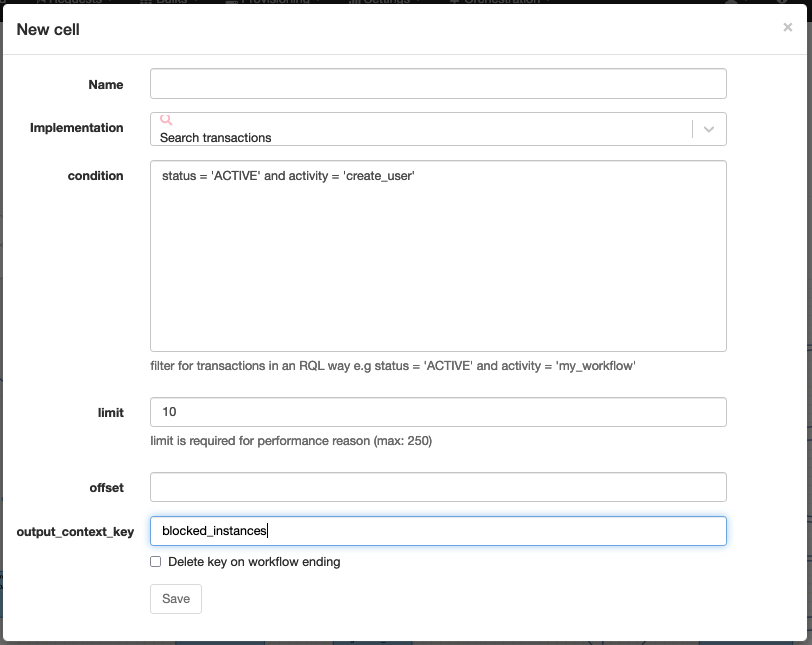
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| query | The query to execute. |
| limit | The maximum number of instances to return. |
| offset | The offset of the first instance to return. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
CSV file
Technical name: create_csv
Create and attach a CSV file to the current request.
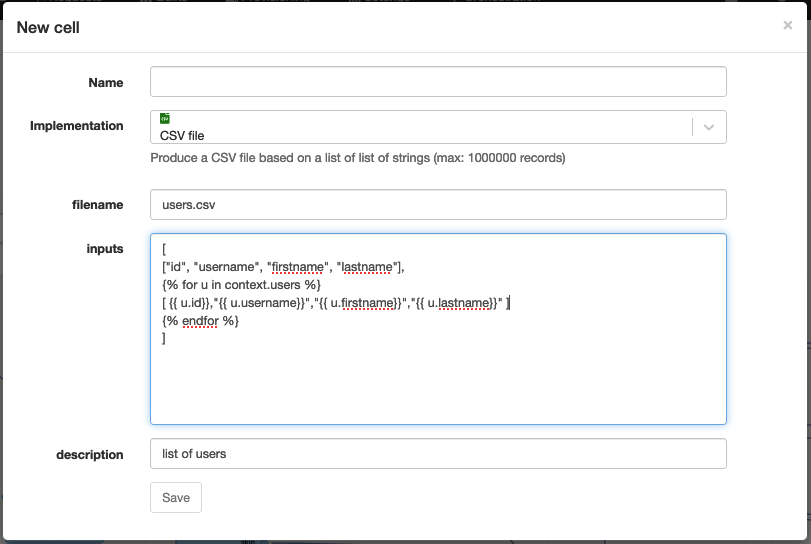
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| filename | The name of the CSV file to create. |
| inputs | The list of inputs to use to generate the CSV file. |
| description | The description of the generated document. |
Excel file
Technical name: create_excel_sheet
Fill an Excel sheet with data and attach it to the current request.
The base has to be stored in the templates of the platform. So it can contains all sort of data / elements, they will be kept in the generated Excel file.
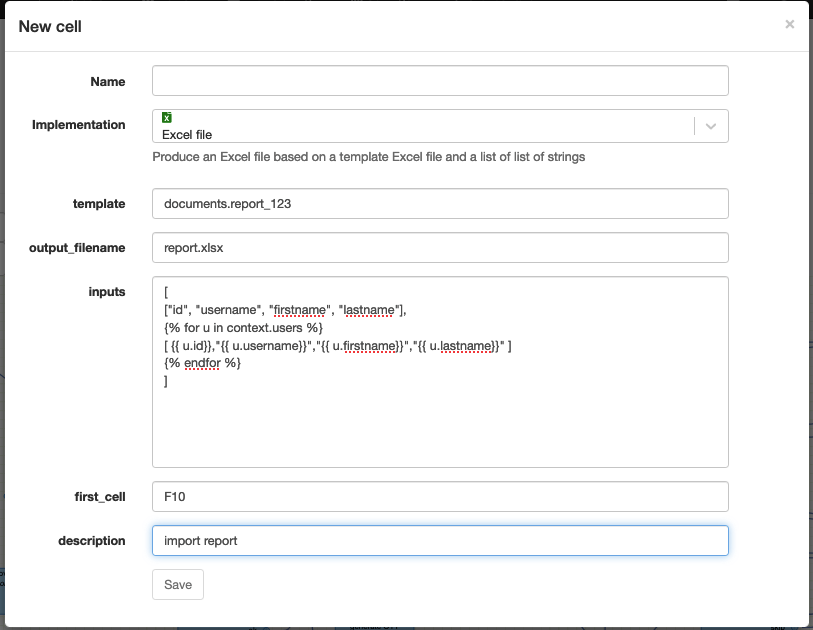
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| template | The name of the Excel template to use. |
| output_filename | The name of the generated Excel file. |
| inputs | The list of inputs to use to fill the Excel file. |
| first_cell | The first cell of the Excel sheet to fill. It may also contains a reference to another sheet (e.g Sheet2!A8) |
| description | The description of the generated document. |
Powershell
Technical name: powershell
Execute a Powershell script in a dedicated docker container wired to the platform.
There is a limit on the number of running containers per platform: (2 * the number of CPU's) + 1. A timeout of 2 minutes waiting for a container to be available. And a timeout of 5 minutes for the execution of the script.
The output of the script is limited to 4MB.
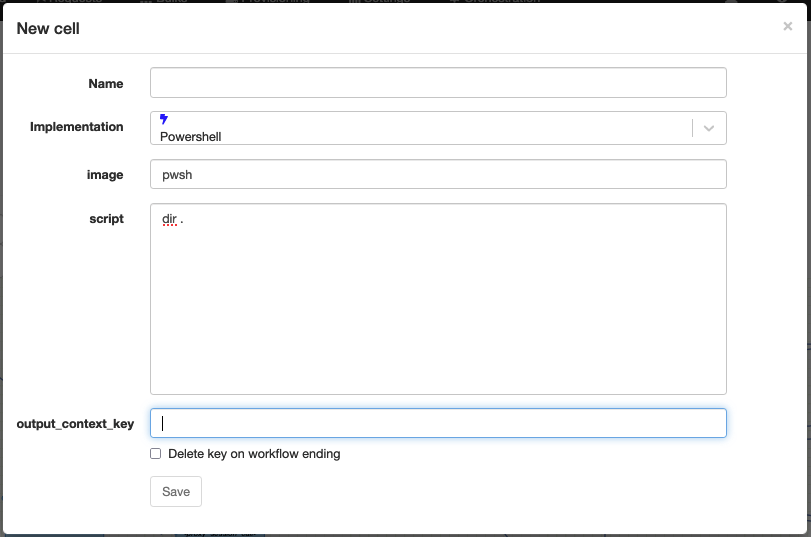
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| image | The docker image to use. |
| script | The Powershell script to execute. |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
(S)FTP
Technical name: ftp
Execute an FTP command on a FTP or SFTP server. (incl. uploading / downloading files)
The FTP server has to be defined in the APIO core configuration as a TCP gateway with url scheme of ftp:// or sftp://.
TIP
If a file is not found on the FTP server while trying to download it, and the output "not_found" is connected, the workflow will continue on this output.
WARNING
The files can be downloaded / uploaded from the APIO core filesystem but it may cause troubles if the workflow ran on a different node than the one where the file is stored. Or if the workflow stops and restarts on a different node.
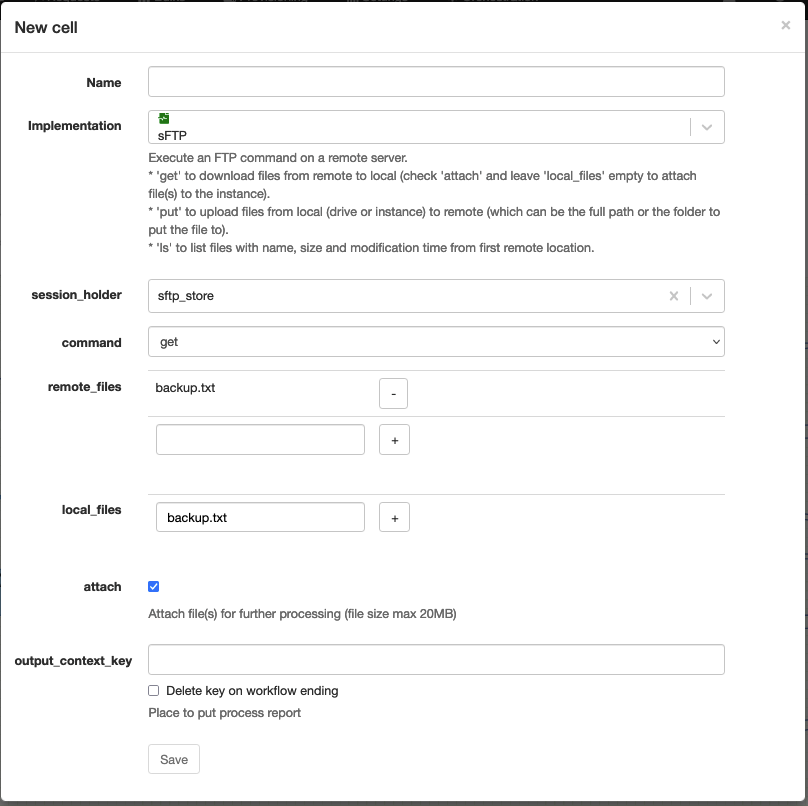
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| session_holder | The session holder to use. |
| command | The FTP command to execute. * get: to download a file * put: to upload a file * ls: to list a remote directory |
| remote_files | The list of remote files to use. * For get and put commands, it's the list of remote files to download / upload. * For ls command, it's the list of remote directories to list. |
| local_files | The list of local files to use. * For get and put commands, it's the list of local files to download / upload to. |
| attach | If set to true, the downloaded files are attached to the current request. Use the local file system otherwise |
| output_context_key | The context variable to assign the result to. |
Go to
Technical name: goto
Jump to another node in the workflow. This can be useful when multiple path converge to a single set of nodes (e.g a set of nodes to handle errors). It avoids cluttering the workflow with multiple arrows to the same set of nodes.
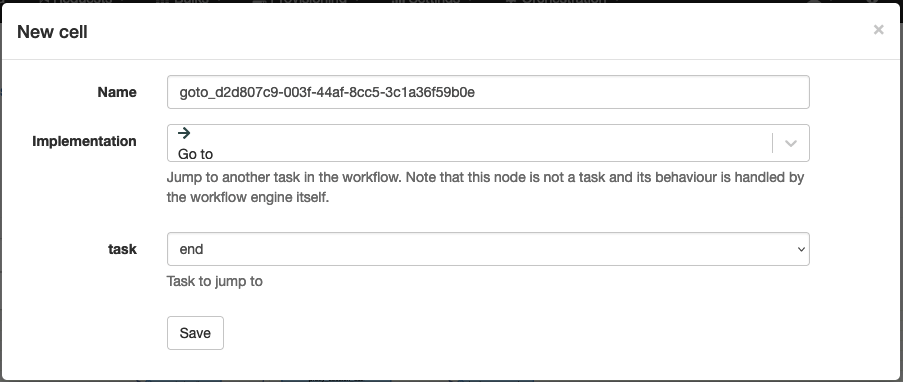
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| target | The name of the node to jump to. |
Note
Technical name: note
A note is a special node without any logic, entrypoint nor output. It's used to add a comment or a description in the workflow.
TIP
One can put a note with the same background color than a set of nodes to describe a feature or a behaviour accomplished by a subset of nodes inside a workflow.
Entity
Technical name: entity
Represents an external entity in the workflow. This node is used to symbolize the external process of an entity which is not managed by APIO core.
Wait Callback
Technical name: wait_callback
This node suspend the execution of the current workflow. Execution can be resumed by Resume Execution node.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| register_async_external_id | This ID must be used to trigger the workflow resume via the callback endpoint or the Resume Execution node |
| async_output_context_key | The callback data (i.e. the content attribute of Resume Execution node) will be stored in this context key when the workflow resumes. |
| timeout | if no callback is received within specified timeout the workflow will go in error state. If not specified the workflow can stay suspended forever. |
Resume Execution
Technical name: resume_execution
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| callbackId | callback ID for resuming the suspended workflow. |
| content | Data that will be passed to the workflow when it resumes. (see async_output_context_key attribute of Wait Callback) |
