Authentication
APIO core supports multiple authentication mechanisms. You can use them to authenticate your users and to authenticate your API calls.
At the end of each authentication process, the user gets a JWT token. The JWT token is used to authenticate the API calls by adding it to the Authorization header (Bearer authentication scheme) of the HTTP requests.
INFO
Refer to the configuration documentation to configure the authentication mechanisms.
Local users
Local users are users that are stored in the database of the APIO core. They are the default users of the APIO core. They are used to authenticate the users of the APIO core UI and to authenticate the API calls.
On the login page, they use their username and password to authenticate.

Broadsoft users
The Broadsoft platform can be integrated as IdP for the APIO core users. So, the users of the Broadsoft platform can be used as the users of the APIO core, using the same username and password.
Login API
POST /api/v01/auth/login HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.com
Content-Type: application/json
{
"username": "user",
"password": "password"
}Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{
"access_token": "...",
"refresh_token": "..."
}Response when the user has an M2M token set
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{
"access_token": "...",
"refresh_token": "...",
"token": "..."
}TIP
The token is the M2M token of the user. It is meant to be immutable and it can be used as the access token for the API calls.
Sequence for regular login

Single Sign-On (SSO)
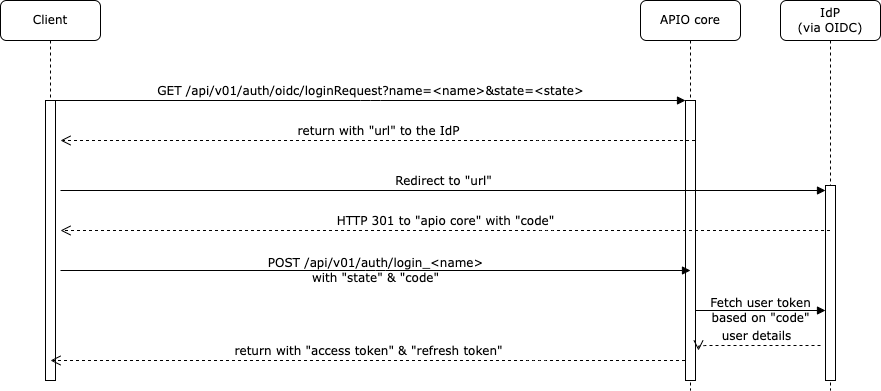
APIO core supports SSO authentication using the OpenID Connect and SAML . It allows you to use your existing identity provider to authenticate your users in the APIO core.
On the login page, they use the button of the identity provider to authenticate.
Sequence for OIDC authentication
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
APIO core supports two-factor authentication (2FA) using email and TOTP (Time-based One-Time Password).
The 2FA is optional and can be enforced for all users with a mail address using the Force 2-factor auth. configuration parameter in the GUI section (see configuration documentation).
Email 2FA
To be able to use the email 2FA, the 2-factor auth. email template configuration parameter in the GUI section (see configuration documentation) must be set.
Then a user can enable 2FA in the user profile page of the APIO core UI.
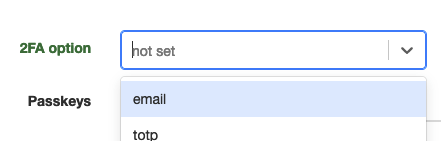
After a successful login, the user receives an email with a 2FA code. The user has to enter the 2FA code to authenticate.
TOTP 2FA
To be able to use the TOTP 2FA, the 2-factor auth. TOTP issuer configuration parameter in the GUI section (see configuration documentation) must be set.
Then a user can enable 2FA in the user profile page of the APIO core UI.
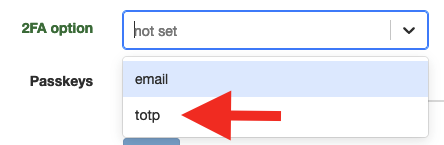
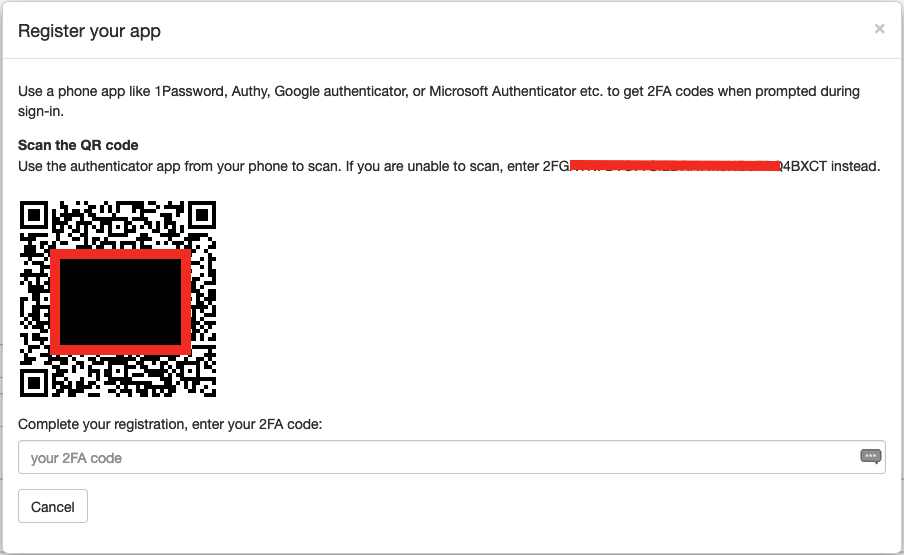
After a successful login, the user has to enter the 2FA code generated by the TOTP application (e.g Google authenticator) to authenticate.
Login response when Two-Factor Authentication is required from the user
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{
"2fa_payload": "...",
"option": "email | totp"
}| option | description |
|---|---|
| The user has to enter the 2FA code sent by email. | |
| totp | The user has to enter the 2FA code generated by the TOTP application (e.g Google authenticator) |
Then the client is supposed to send the 2FA code to the 2FA API.
POST /api/v01/auth/2fa HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.com
Content-Type: application/json
{
"2fa_payload": "...",
"code": "..."
}The response contains the JWT tokens.
Sequence for login with 2FA required

Passwordless login API (using WebAuthN)
refer to the Web Authentication API documentation
Passwordless login is a login method that uses a physical device (e.g. a security key) to authenticate the user. The user does not need to enter a password to authenticate.

Refresh token
The access token can be used to make API calls for a short period of time. After that, the access token expires and the client needs to use the refresh token to get a new access token.
GET /api/v01/auth/access_token HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.com
Authorization: Bearer <refresh_token>Response
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{
"access_token": "...",
"refresh_token": "..."
}INFO
A new refresh token is sent only when the refresh token is about to expire.
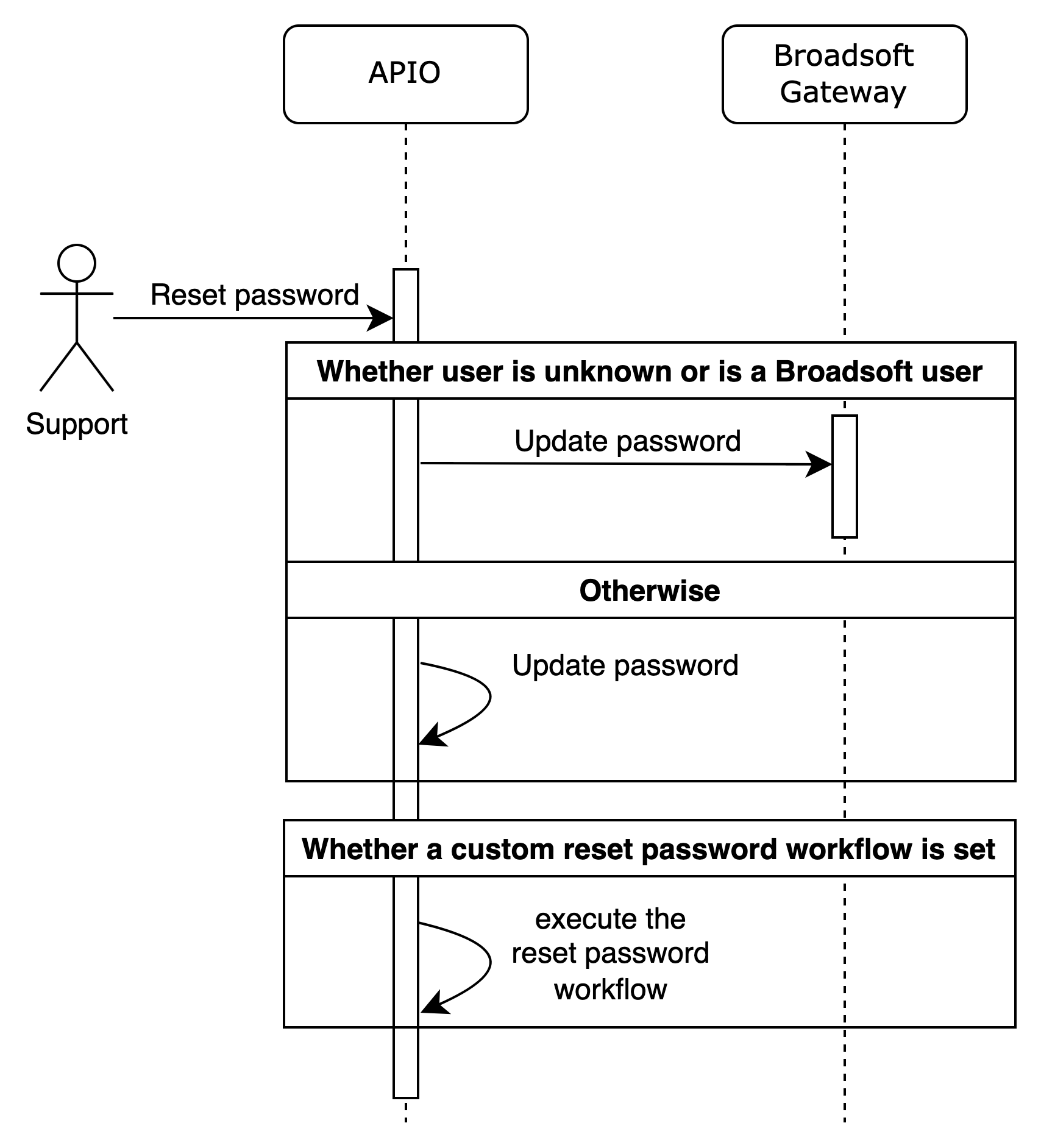
Reset password
Local users and Broadsoft users (if the Broadsoft platform is integrated as IdP) can reset their password using the reset password API.
The reset password API sends an email to the user with a link to reset the password. By default the link is valid for 20 minutes.
The email template is selected by the reset_password_email_template configuration parameter in the GUI section (see configuration documentation).
The template name is mails.reset_password by default, but it can contain the following variables to customise the email based on criteria:
| Variable | Origin | Description |
|---|---|---|
{ui_id} | Request body | The ID of the UI interface. This to align the branding of a different mail with a different portal. |
{ui_language} | Request body | The language of the UI interface. |
{proxy} | Request body | A proxy name used when multiple Broadworks proxies coexists in the same platform. |
{language} | User profile | The language of the user. |
e.g mails.reset_password.{ui_id}.{language} or mails.reset_password.{ui_id}.
Such reset password email can only be sent once every 5 minutes.
WARNING
For security reasons, the reset password API does not return any error if the user does not exist.
INFO
Other users (SSO users) can reset their password using the reset password API of the IdP.
Customisation
The reset password process might require some customisation to fit specific needs (e.g. custom email API, setting user password in different places).
The reset password API process can be configured to use a custom process by setting the Reset password notification workflow and Post-reset password workflow configuration parameter in the GUI section (see configuration documentation).
Notification flow
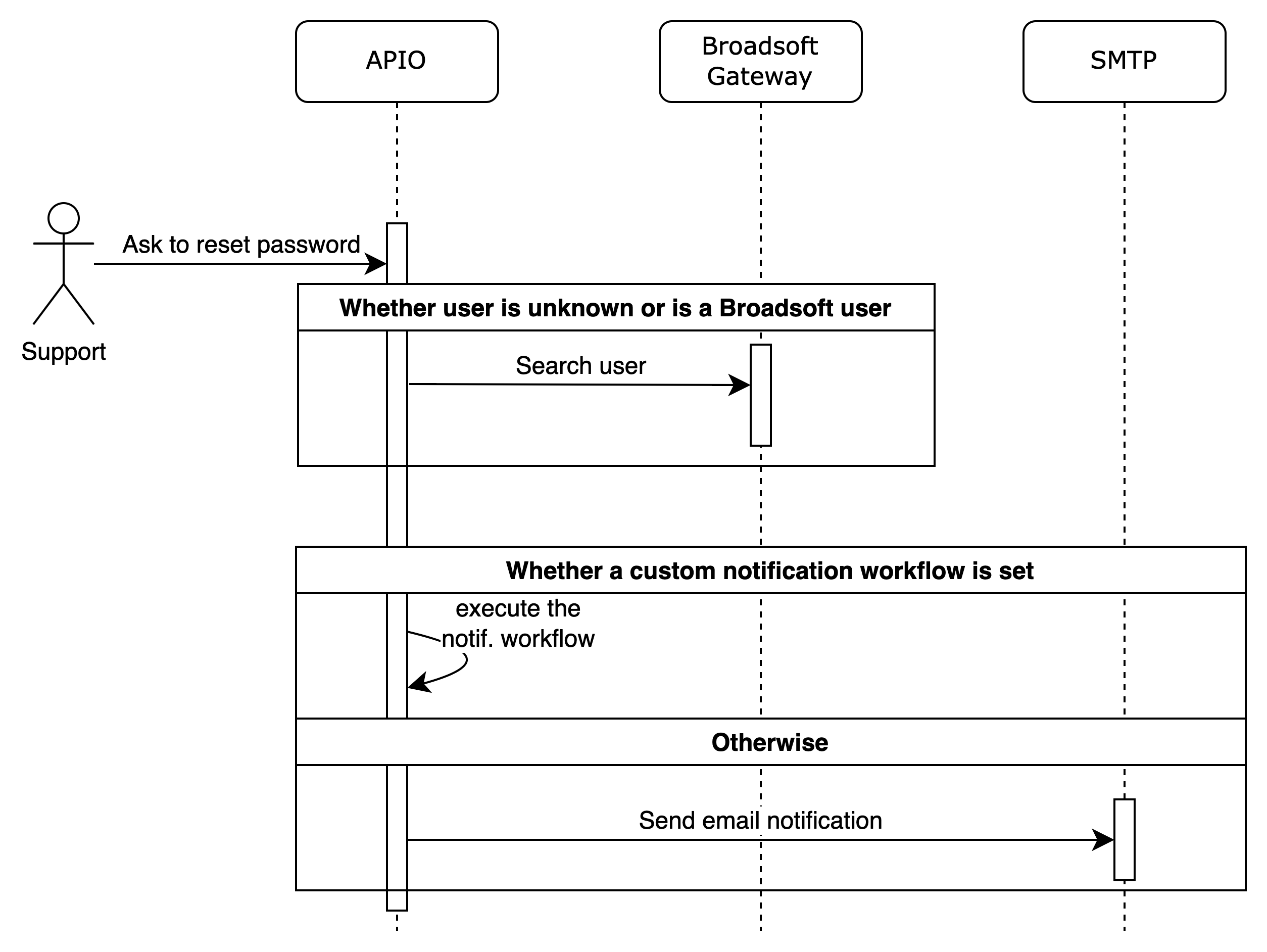
Execution flow